Decision Making Process
- The systematic approach to the mental process used by pilots to consistently determine the best course of action in response to a given set of circumstances
- Effective ADM is not just about reacting to emergencies; it’s a continuous process applied during all phases of flight, from pre-flight planning through post-flight analysis
PAVE Checklist
PHAK 2-8
Pilot
currency, proficiency, physical health, emotional state
IMSAFE
Aircraft
airworthiness, equipment, performance
ARROW/PECM AVIATE ATOMATOFLAMES/FLAPS
Environment
weather, terrain, airport, runway, airspace, night
NWKRAFT
External Pressures
passengers, work, get-there-itis
3P Model
PHAK 2-15
Percieve
Process
associated risks evaluate impact on safety of flight
Perform
best course of action mitigate or eliminate risk
5P Check
PHAK 2-13
Plan
weather, route, airports, ATC, regulations
Plane
airworthiness, equipment, performance, fuel, systems
Pilot
physical and mental condition, knowledge, proficiency
Passengers
breifing, experience, comfort, pressures
Programming
navigation, communication, autopilot, workload
Hazard & Risk Identification
Flight Risk Assessment Tool
PHAK 2-4
Hazard
a real or perceived condition, event, or circumstance that a pilot encounters
Risk
an assessment of the single or cumulative hazard facing a pilot
Risk Assessment Matrix
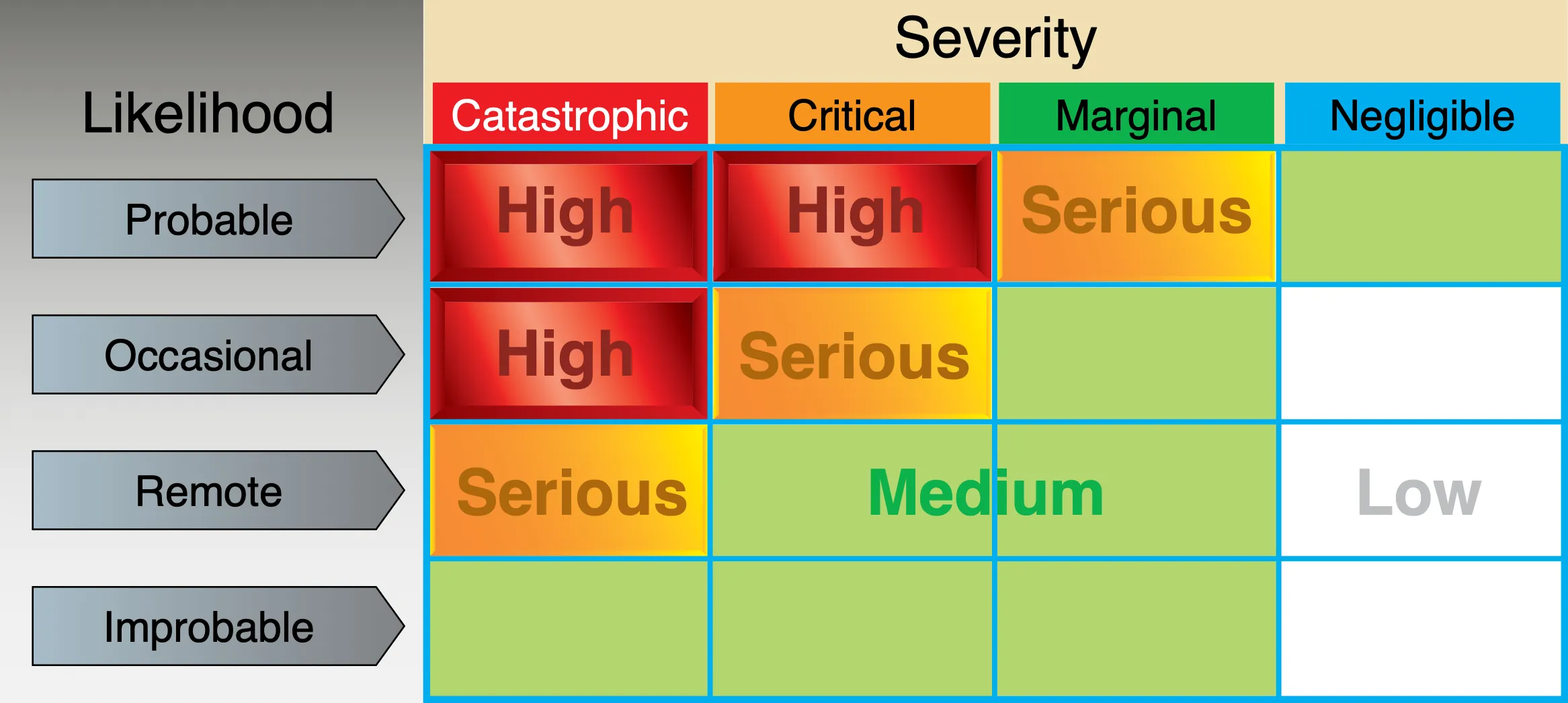 PHAK Figure 2-5
PHAK Figure 2-5
Hazardous Attitudes
PHAK 2-5
Anti-authority
Resenting rules and procedures “Don’t tell me what to do”
Antidote – follow the rules; they are usually right
Impulsivity
Acting without considering consequences “Do something – quickly!”
Antidote – Not so fast; think first
Invulnerability
Believing accidents only happen to others “It won’t happen to me”
Antidote – It could happen to me
Macho
Trying to prove oneself by taking risks “I can do it”
Antidote – Taking chances is foolish
Resignation
Feeling powerless to make a difference “What’s the use?”
Antidote – I’m not helpless; I can make a difference